Extracting Diurnal Patterns of Real World Activity from Social Media
 Published on March 30, 2013.
Published on March 30, 2013.
Our most recent work got accepted to ICWSM 2013! See the publications page for the full paper.
Here is the abstract:
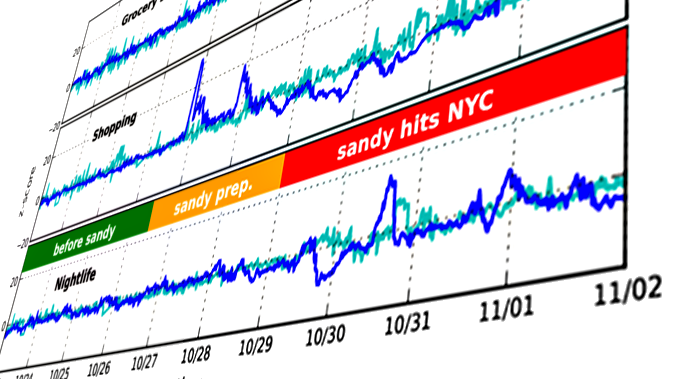
In this study, we develop methods to identify verbal expressions in
social media streams that refer to real-world activities. Using
aggregate daily patterns of Foursquare checkins, our methods extract
similar patterns from Twitter, extending the amount of available content
while preserving high relevance. We devise and test several methods to
extract such content, using time-series and semantic similarity.
Evaluating on key activity categories available from Foursquare (coffee,
food, shopping and nightlife), we show that our extraction methods are
able to capture equivalent patterns in Twitter. By examining rudimentary
categories of activity such as nightlife, food or shopping we peek at
the fundamental rhythm of human behavior and observe when it is
disrupted. We use data compiled during the abnormal conditions in New
York City throughout Hurricane Sandy to examine the outcome of our
methods.









